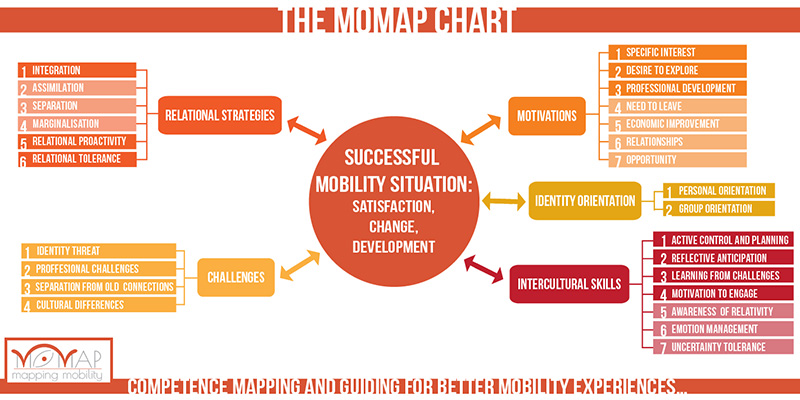
| Desire to explore: | A genuine interest in discovering new places, new environments. The instinct of the explorer
(example: “I’ve always wanted to see other countries”) |
|---|---|
| Specific interest: | A genuine interest in one particular destination – be that a country or a professional path Professional development Engaging in mobility as a means to develop professional skills Relationships. Engaging in mobility because of someone else
(example: “I followed my wife to Mexico”) |
| Opportunity: | Engaging in mobility because an opportunity presented itself
(example: “My boss told me about an international exchange program, so I applied”) |
| Economic Improvement: | Expecting an improvement of the economical condition through mobility
(example: “Going away was the only hope of earning decent money”) |
| Need to leave: | An external need to depart from the home environment, triggered by unpleasant life conditions, or even threats.
(example: “I knew I had to get away if I wanted to do something with my life”) |
| Group identity orientation: | A tendency to identify oneself dominantly though memberships in different social groups such as nationality, religion, ethnicity, social class. |
|---|---|
| Personal identity orientation: | A tendency to identify oneself dominantly through individual characteristics, achievements and life experiences. |
| Active control and planning: | Capacity to take action to solving problems Reflective anticipation Skills of developing patterns and explanations from observation. |
|---|---|
| Learning from challenges: | Capacity to reframe difficult tasks as learning opportunities and as opportunities for change. |
| Motivation to engage: | An attitude of resisting the need for retreat and for avoiding potentially disturbing, difficult situations |
| Awareness of relativity: | Awareness of cultural differences. |
| Emotion management: | Capacity to manage one’s emotions and not to be carried by them, not to be imprisoned by them. It is not the same as the exteriorisation of emotions or the tendency to display them |
| Uncertainty tolerance: | Tolerance of uncertain situations |
| Cultural Differences: | Difficulties that arise from the difference between cultural reference frames. Differences include: gender roles, different approaches to hierarchy, difference in ways of thinking, differences in customs. |
|---|---|
| Identity Threat: | The threats to identity can imply the perception of feeling different, sticking out, facing stereotypes or even racism against one’s own cultural group. |
| Professional challenges: | Concerns related to finding a proper job, performing well, making a good living out of it. |
| Separation from old connections: | Conflicts and misunderstandings marking the separation from the primary social relations of family and friends from the old environment. |
| Integration: | Maintaining social relations with members of the new environment and the old cultural environment as well. |
|---|---|
| Assimilation: | Valuing connections with the new environment and losing connections with the old environment. |
| Separation: | Not having relations with either members of the original or the new environment |
| Marginalisation: | Conflicts and misunderstandings marking the separation from the primary social relations of family and friends from the old environment. |
| Relational proactivity: | While the previous items give the direction of the social activity, relational proactivity expresses the intensity of the relational engagements: how much effort one puts in establishing and maintaining social relations. |
| Relational tolerance: | Unlike proactivity, it expresses the lack of tolerance and the refusal of making connections to people in the new environment. It is a resented position where one purposefully gives up the desire to connect. |